How to record computer's playback under Linux
Posted on septembre 29, 2020 in computer-science
Let us suppose that you want to record the audio playback of your computer without any external recording system.
A poor man's solution would be to plug a microphone in the audio input jack and record from it, say with the sound editor Audacity. Beside the bad quality of the sound recording, a drawback of this approach is that it is going to pick up any noise in the room, unless you have two separate input (mic) and output (headpĥone) jacks on your computer, in which case you can use male-male jack cable to connect both.
Here is a better solution, using the Audacity and PulseAudio Volume Control:
- Launch both
audacityandpavucontrol. -
In Audacity.
-
Open the menu
Edit/Preferences:- In the
DevicesTab,- select 'ALSA' in
Interface/Host. - select 'pulse' in
Playback/Device.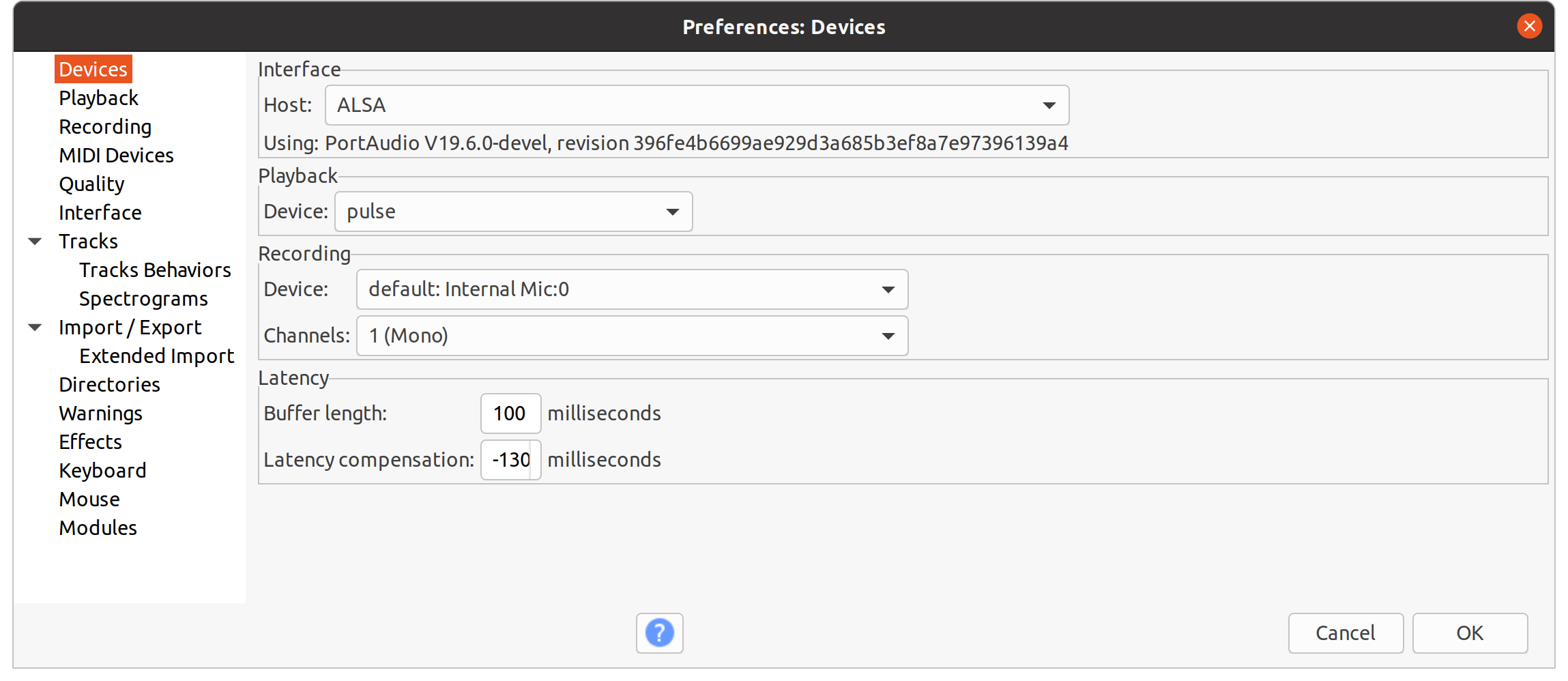
- select 'ALSA' in
- In the
Recordingtab, make sure thatSoftware playthrough of inputis not selected.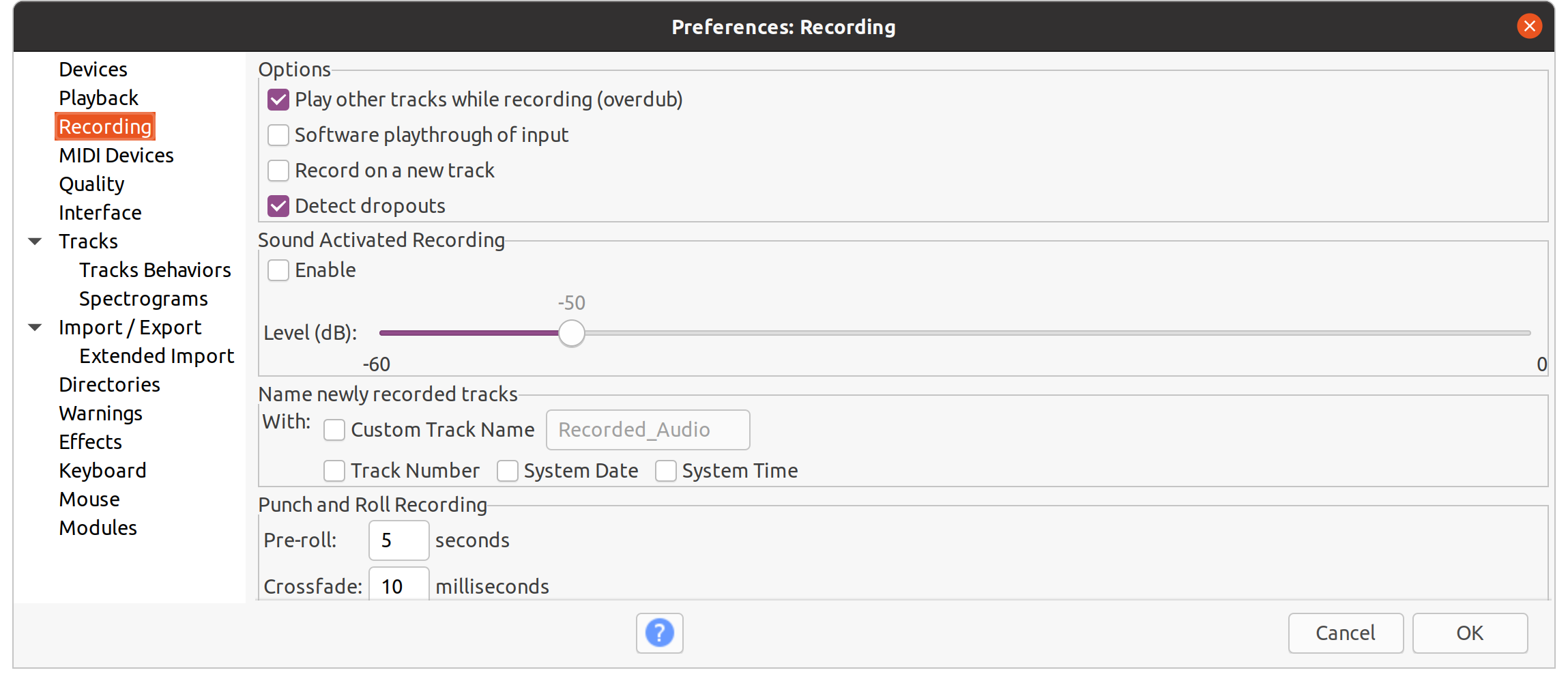
- Close the
Preferenceswindow and start recording (Shift+R)
- In the
-
In PulseAudio Volume Control:
-
In the
Configurationtab, underBuilt-in audio, select `Analog Stereo Duplex``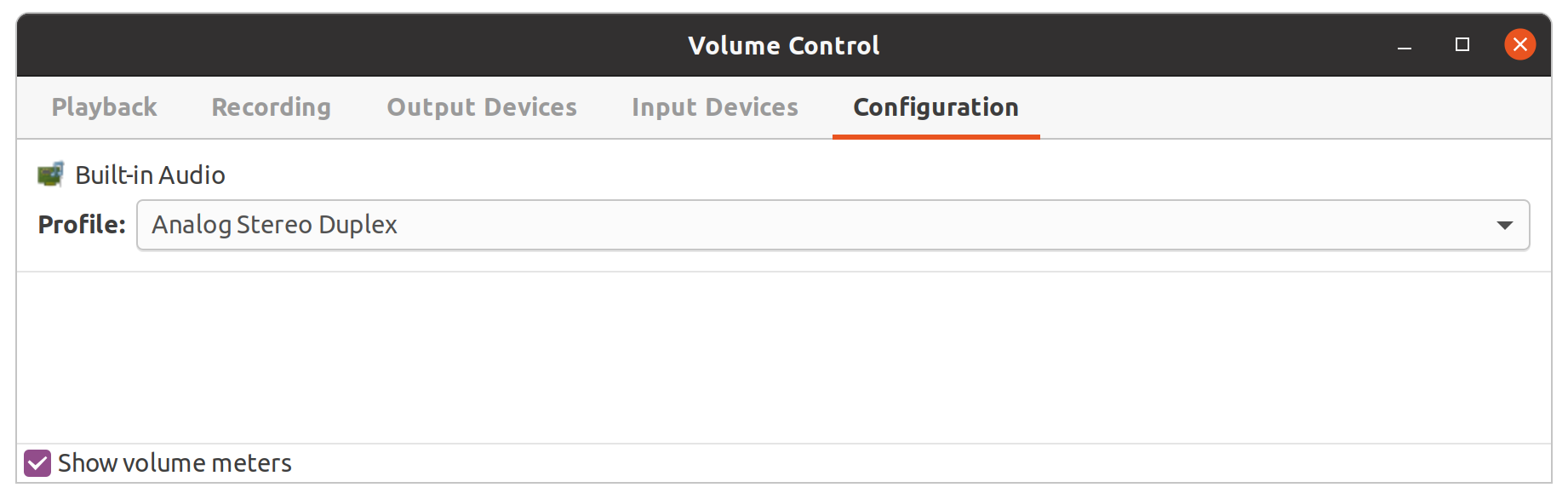
-
In the
Recording Tab, showing 'all streams', you should see the Audacity stream (Audacity must be in recording mode!), and Audacity should be recording the audio playback of the computer.
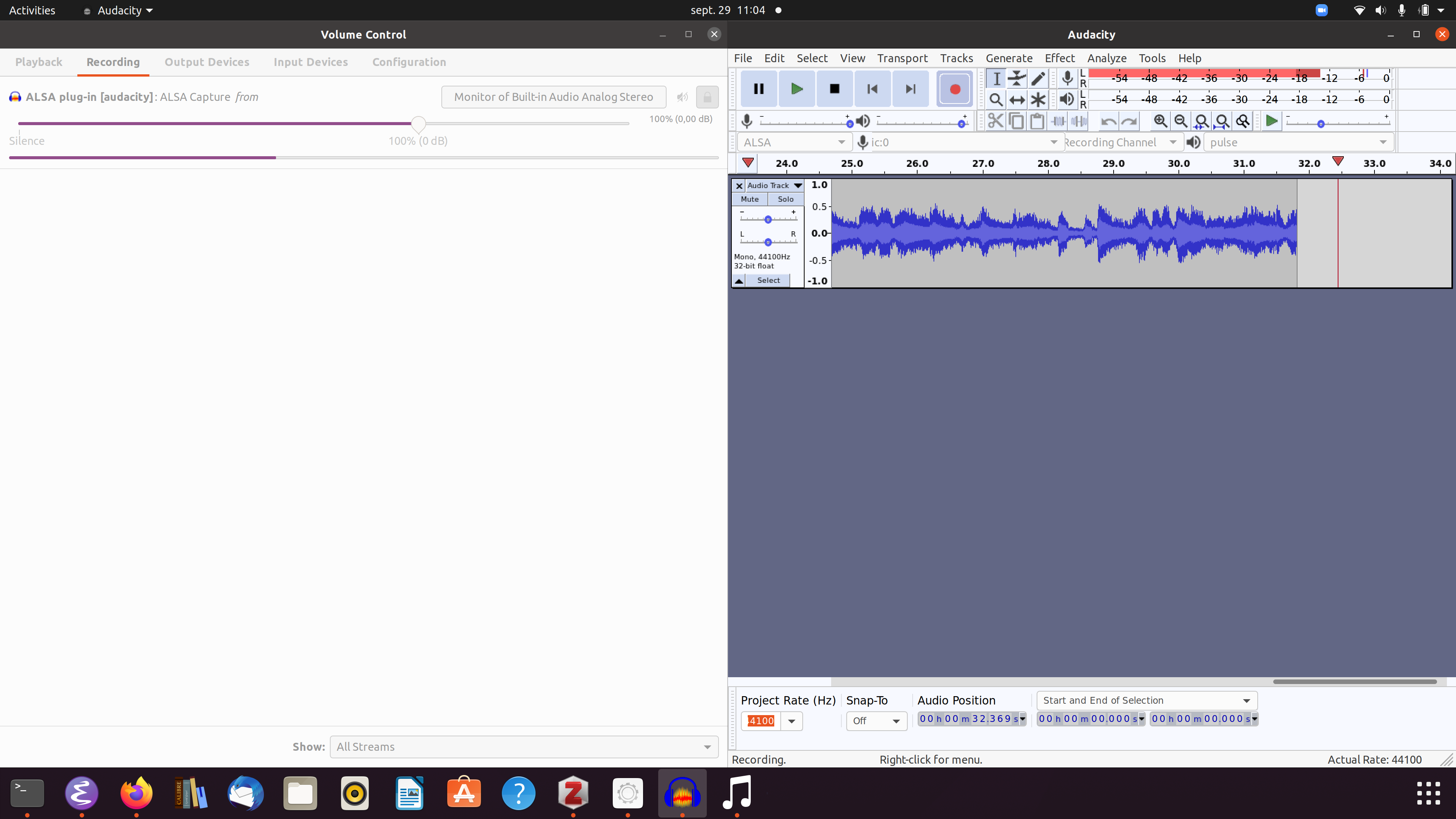
Remark: In Ubuntu 20.04, I am using versions 2.3.3 of audacity and version 4.0 of pavucontrol.
Recommended reading: How to use Pulse to manage sound on Linux
Other possible approaches
-
Use
alsamixerto enable the loopback device ('y':disable 'e': enable). -
Use
alsaloop -
Use the
snd-aloopkernel module to set up a virtual audio loopback device (see https://sysplay.in/blog/linux/2019/06/playing-with-alsa-loopback-devices/)modprobe snd-aloop arecord -f cd -D loop > recording.wav aplay -f cd -D hw:0,0 recording.wav
pactl load-module module-null-sink sink_name=MySink PULSE_SINK=MySink parec -v -d MySink.monitor --file-format=wav recording.wav